The future is here, sort of. Companies have staked out urban landscapes to test autonomous last-mile delivery systems on the streets and mobile food delivery robots on campus sidewalks. Ultimately for ecommerce merchants, the results could mean faster deliveries with more options for their customers.
Here is a list of companies developing autonomous delivery robots and systems. Nearly all of these companies currently have live beta programs.
Starship Technologies
Starship Technologies offers autonomous robots for stores, restaurants, and campuses. Starship robots can carry items within a 4-mile radius. Starship’s robots weigh no more than 100 pounds, move at pedestrian speed, and navigate around objects and people. The cargo bay is mechanically locked throughout the journey and can be opened only by the recipient with their smartphone app. The location of the robots is tracked, so customers know exactly the location of an order and receive a notification at the time of arrival. Services have been launched for Arizona State University, University of Wisconsin, Modesto (California), and Northampton (U.K.).
—
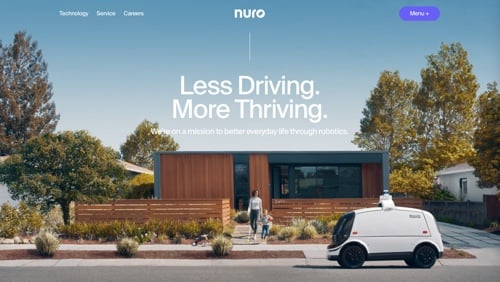
Nuro
Nuro produces custom autonomous delivery vehicles for neighborhoods. Its main vehicle, the R2, features 360° cameras, Lidar, short and long-range radar, and ultrasonic sensors. Nuro has formed several partnerships in Houston: Domino’s for pizza deliveries, CVS for prescription deliveries, and Walmart for grocery deliveries. Recently, FedEx has made a long-term commitment to use Nuro’s autonomous bots for last-mile delivery at scale. Testing has already begun with FedEx in Houston.
—
Udelv
Udelv completed its first autonomous delivery on public roads in January 2018. Since then, it’s been developing automated delivery vehicles for retailers and shippers. The automated vehicles can drive on highways, carry over 800 pounds of payload, and gather operational data to improve logistics. Udelv recently partnered with Intel’s Mobileye, incorporating Mobileye Drive into the next-generation Udelv autonomous delivery vehicles called “Transporters.” The companies plan to produce more than 35,000 Mobileye-driven Transporters by 2028, with commercial operations beginning in 2023.
—
Kiwibot
Kiwibot produces automated robots for a food delivery urban infrastructure. Initially, the startup provided food deliveries for the University of California, Berkeley. Now, the company also delivers to parts of the city of Berkeley, on the Stanford University campus in Palo Alto, and in San Jose. Since its start in 2017, Kiwibot has made over 150,000 deliveries. Its goal is to bring the cost of delivery down as low as possible and ensure that any product purchased can be delivered within an hour or less.
—
Eliport
Eliport is a Barcelona-based start-up tackling last-mile logistics by providing fleets of small ground-based, robotic delivery machines for urban areas. These robots are autonomous, and they travel on pavements and in pedestrian zones at walking speed. Eliport robots can load and unload without human interaction.
—
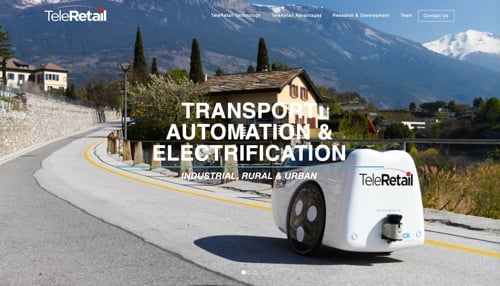
TeleRetail
TeleRetail is a Swiss start-up developing Aito autopilot software and delivery vehicles, such as its Pulse 1, for automated urban, suburban, and rural logistics. The small Pulse 1 minimizes the energy and space requirements of local logistics while avoiding harmful emissions. The solar-powered Range+ version covers almost unlimited distances. TeleRetail’s main objective is to help main street shops and small businesses offer the same level of convenience as ecommerce giants such as Amazon. TeleRetail has been financed, in part, by grants, including $2 million from the European Space Agency.
—
Postmates Serve
Postmates is a food delivery app and service owned by Uber. Its Serve robot is designed for safe, autonomous navigation on urban sidewalks. Serve navigates using Lidar and communicates with customers through an interactive touchscreen. Serve bots are all-electric with a 50-pound capacity. Serve’s initial launch has been in Los Angeles and San Francisco.
—
Robby Technologies
Robby Technologies was founded by two PhDs, each with 15-plus years of experience in computer vision and robotics, and selected by accelerator Y Combinator in 2016. In 2019, Robby Technologies partnered with PepsiCo to deliver snacks and beverages via a fleet of self-driving Robby robots on the University of the Pacific campus in Stockton, California.
—
BoxBot
BoxBot, founded by ex-Uber and Tesla engineers and backed by Toyota AI Ventures, is developing a last-mile delivery system for ecommerce packages and deliveries. BoxBot’s system includes self-driving delivery vans and automatic loading systems. Recipients can schedule their delivery at a time of their choosing (including evenings), giving ecommerce customers an option that helps them better plan their day and keep their purchases safe. When BoxBot’s autonomous vehicle arrives, customers receive a text message alert with a unique code they can use to retrieve packages from its parcel lockers. BoxBot currently has a partnership with logistics operator OnTrac.
—
Amazon Scout
Amazon Scout is an electric delivery system designed to get packages to customers safely using autonomous delivery devices. Scout bots are the size of a small cooler and roll along sidewalks at a walking pace. Scout initially launched testing to a neighborhood in Snohomish County, Washington. The autonomous delivery system has since expanded to Atlanta, Georgia, and Franklin, Tennessee.